
Install jenkins on ubuntu
Introduction
Jenkins is one of the most popular open-source continuous integration and continuous delivery servers available today. It provides lots of plugins for building deploying and automating plugins. With Jenkins, organizations can accelerate the software development process by automating it. Jenkins manages and controls software delivery processes throughout the entire lifecycle, including build, document, test, package, stage, deployment, static code analysis and much more.
Installing Jenkins
Jenkins provides an Ubuntu repository for the installation packages and we will install Jenkins from this repository.
|
1 2 |
wget -q -O - https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian/jenkins-ci.org.key | sudo apt-key add - sudo sh -c 'echo deb http://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable binary/ > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/jenkins.list' |
Update the repository and install Jenkins.
|
1 2 |
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install jenkins |
Configure Jenkins
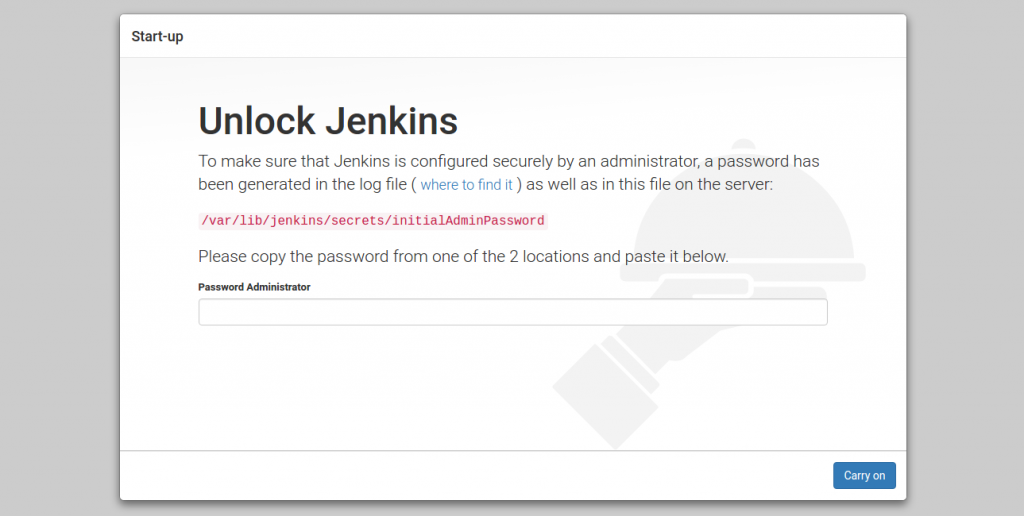
After installation is completed go to localhost:8080 we should see “Unlock Jenkins” screen, which displays the location of the initial password.
to get the hash password go to /var/lib/jenkins/secrets and run sudo vi initialAdminPassword
copy/paste the password in the “Administrator password” input.
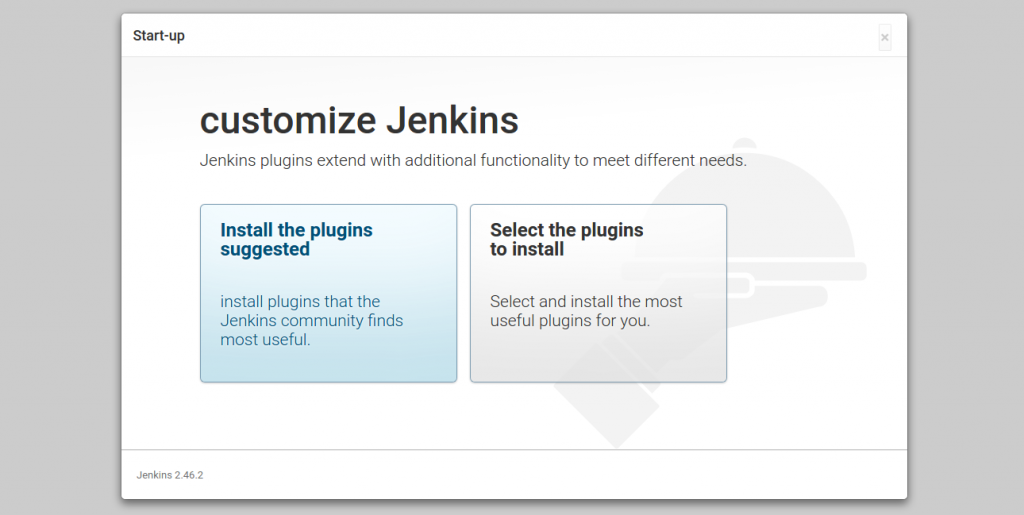
Now select appropriate option to install plugin. You can choose to install suggested plugins or select required plugins options. To get a good foundation for later use. Choose “Install Suggested Plugins”.
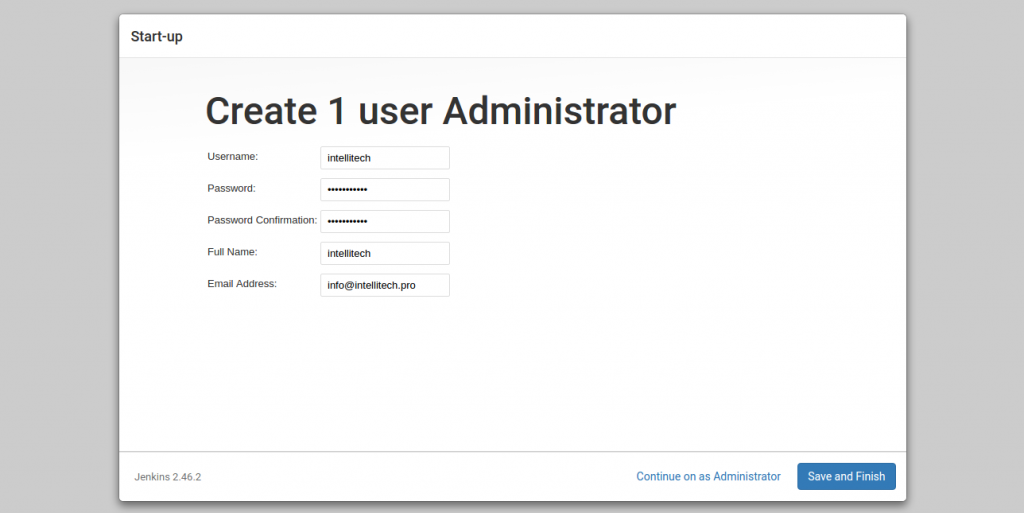
After plugin installation, we have to create a new admin account. Type in your admin username, password, email etc. and click on “Save and Finish”.
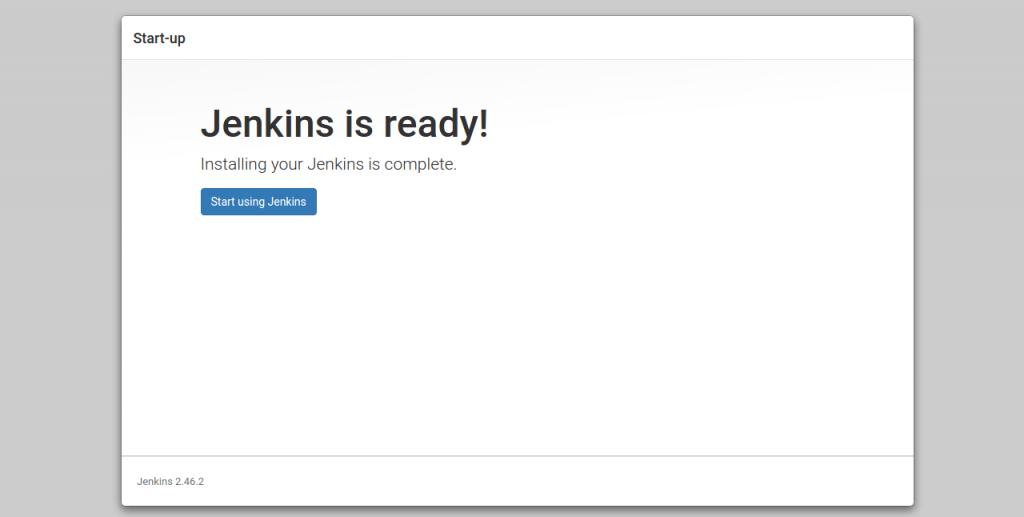
Configuration completed and Jenkins is ready and you can start working with it after clic “Start using Jenkins” button
Now you will be redirected to Jenkins dashboard and show the default Jenkins screen. Jenkins installation and Configuration finished successfully
You can set up Jenkins to watch for any code changes in places like SVN and GitHub, automatically do a build with tools like Ant and Maven, utilize container technology such as Docker and Kubernetes, initiate tests and then take actions like rolling back or rolling forward in production.ata
